Cheat sheet: Google’s 13 top ranking factors
A step-by-step recipe to ranking in Google’s top
It’s no secret that a top Google ranking is made up of over 200 ingredients, or “ranking signals”. And while it may be useful to know what all those ingredients are, the original recipe is an incredibly time-consuming (and a little depressing) read. It’s unreasonably vague in terms of proportions, and it just doesn’t seem doable if you try to follow it line by line. With the news about another Google update or algorithm change rolling out every other week, how can anyone keep up, ever?
But SEO bartenders have their tricks of the trade. The thing is, the 200+ ingredients in Google’s recipe aren’t all equally important. In the cheat sheet below, you’ll find 13 top ranking signals that we’ve seen make the biggest impact on Google rankings ourselves, from over 10 years of experience in the industry. Read on to find out which SEO factors carry the most weight, and get quick how-tos on mixing yourself the ultimate Google mojito. Optimize responsibly! 😉
Equipment
Here are the tools you’ll need to measure and optimize for the top 13 ranking signals in this guide.
2. Google Search Console
3. Copyscape
Links (1.5 oz)
1. Link quality
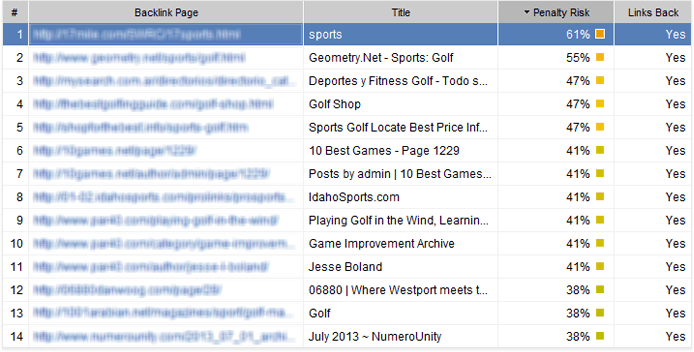
The talk about link quality has been on for years, and most SEO-ers agree it remains the strongest ranking signal for Google. While high quality links can boost your site’s link score (and therefore rankings), lower quality backlinks can get your site penalized (and even out of the SERPs completely).
For the latter not to happen, make sure you run regular link audits so you can spot any dangerous links early and have them removed in time.
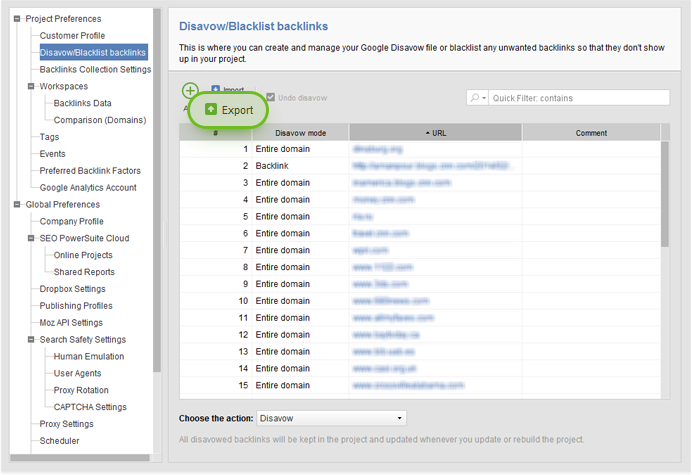
If you don’t hear back from them, or if you’ve got a substantial number of low quality links, disavowing them is your best option. Disavowing is basically telling Google to discard that link (or linking domain) when evaluating your link profile. To disavow backlinks, you’d need to put up a disavow file following certain syntax and formatting rules, and upload the file to Google Search Console.
You can create a disavow file right in SEO SpyGlass in a few clicks. To do that, select the links you’d like to disavow, right-click the selection, and hit Disavow backlinks. Most of the time, you’d want to disavow links on the domain level; so make sure you select Entire domain under Disavow mode. Then, go to Preferences -> Disavow/Blacklist backlinks and hit Export to save the disavow file to your computer, and upload it to Google Search Console.
2. Number of links and linking domains
A few years ago, link count was perhaps the major quality signal for Google. Over time, the search engine learnt to identify the so-called link schemes, or low quality links created solely for the purpose of obtaining higher rankings. Since then, it’s often said that quality comes before quantity for Google — but this is in fact only partly true. The number of links and linking domains still has a massive impact on your ranking potential; it’s just that you can’t afford to have any spammy links in your profile anymore.
In several of its patents, Google suggests that a site’s overall link score (arguably the biggest ranking signal) is made up by individual quality scores passed on to it by every incoming link. That literally means that more links will result in a higher score — as long as they aren’t low quality links, of course.
It’s also important to note that links coming from the same domain (especially site-wide links) carry little weight; Google will often only count one of those links when evaluating your link profile.
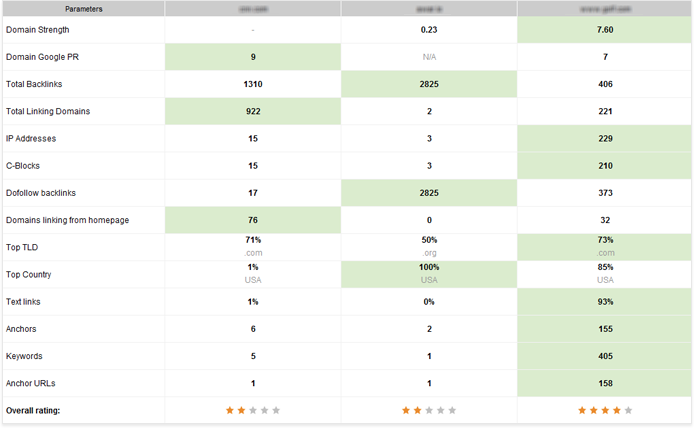
Checking on your top SEO competitors’ link profiles is a good starting point to understand what kind of link scores you are competing against, and how much work is required for you to catch up.
Go to the Projects Comparison module to see how your and your competitors’ link profiles compate. Total Backlinks and Total Linking Domains should give you a good idea on how much improvement your link profile may need, quantity-wise.
To pick the most reputable, high quality prospects, go to the Ranking factors tab, select the prospects you’ve just found, and click Update -> Update ranking factors to get all kinds of quality stats (Alexa rank, Google PageRank, Page and Domain Authority, social signals, etc.) on the link opportunities you’ve found.
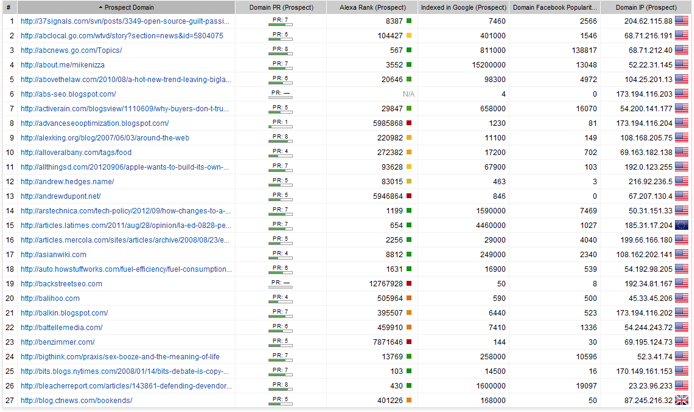
When you’ve singled out top prospects, you can reach out to them right from LinkAssistant. Right-click a contact (or several contacts, if you’ll be sending them a similar message), and click Send email to selected prospects. In your email, feel free to either put up a message of your own or use some of the ready-made email templates, depending on the link building technique you’re using. You can check for replies and manage your correspondence with prospects in the Email module. Once you start to acquire links, remember to verify and manage them in Prospects under the Backlinks tab.
3. Link relevance and diversity
In general, you want your links to be coming from pages whose topic is similar to that of the page you’re optimizing. But how can Google identify relevance, exactly? Primarily, from the backlink’s anchor text. The title of the backlink page can also help to tell what the page is about, although it is a much weaker signal than anchor text.
The concept of relevance is tightly linked to that of diversity. While your backlinks are expected to be semantically relevant to the topic of your page, it’s important to note that too similar anchor texts can get your under Google’s Penguin penalty.
Understandably, there’s no universally right ratio of different kinds of anchor text in your link profile. However, below you can find some averages to give you an idea of what a natural link profile typically looks like.
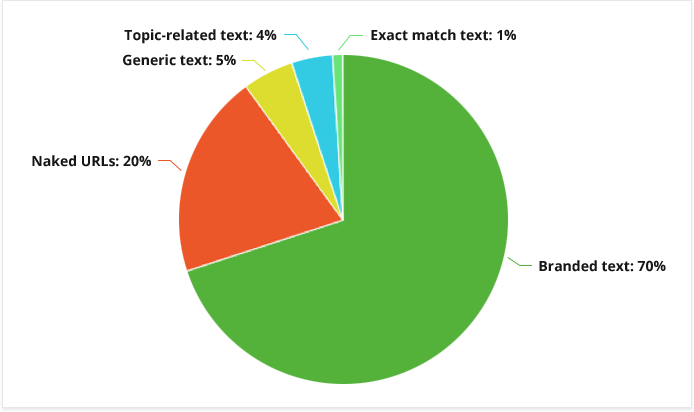
But just as it is with about anything in SEO, it’s best to rely on the link profiles of your top ranking competitors instead of the vague overall averages.
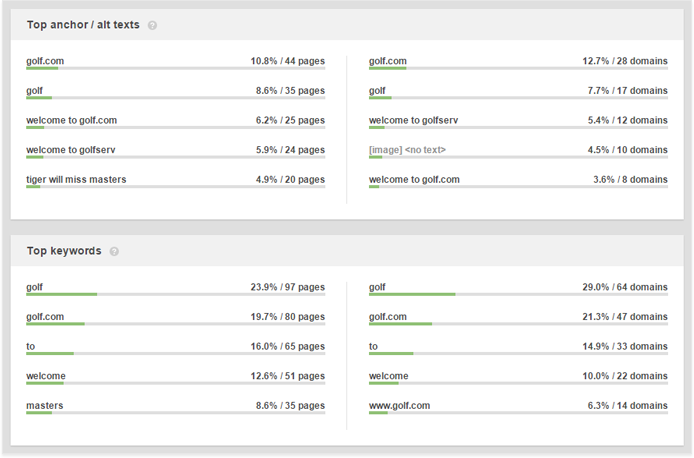
Now, select the backlinks you’ve imported and hit Update -> Get Contact Email. This way, you’ll be able to reach out to webmasters right from LinkAssistant and ask them to make any changes to the links’ anchor text (or contact them regarding any other matter). Once they’ve made the changes you asked for, you can easily verify the links and see what’s changed by clicking the Verfiy button.
On-page SEO (0.75 oz)
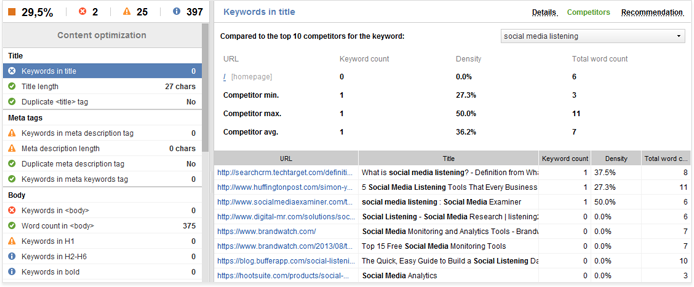
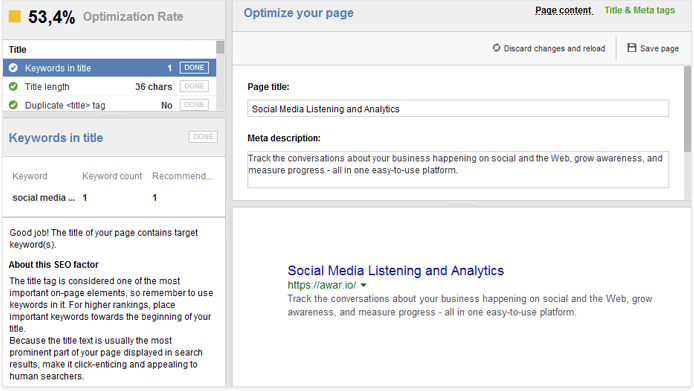
4. Keywords in title and meta description
Your page’s title tag remains the strongest relevancy signal to Google. Make sure to include your keywords or terms semantically related to them in your title; the closer these terms are to the beginning of your title tag, the better.
The meta description generally carries less weight for search engines in terms of relevance. However, using your keywords in the description is still a good practice and can also result in a minor ranking boost for the terms you are targeting.
When you’re done optimizing your page, hit Save page to save the upload-ready HTML file to your hard drive.
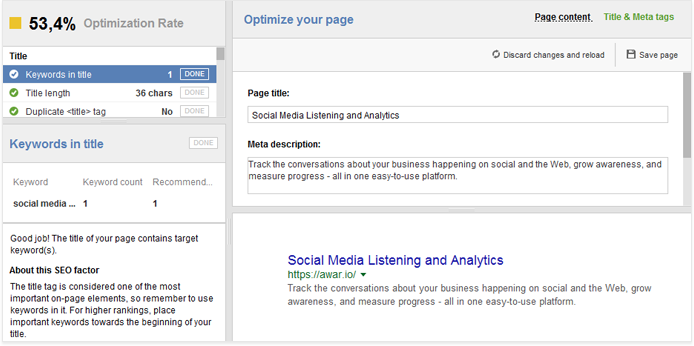
5. Duplicate titles & descriptions
Having duplicate title and meta description tags across several pages can result in Google only picking one of these pages to display in SERPs. To make sure none of your pages compete in search results against each other, remember to create a unique title and meta description for each one.
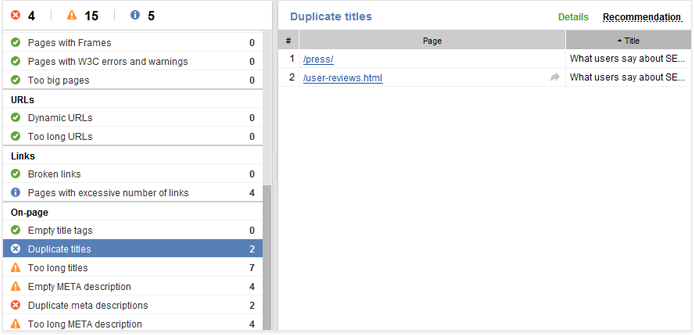
6. Keywords in copy
While it’s undoubtedly true that Google is shifting towards semantic search, that doesn’t mean it’s shifting away from keywords. Far from it. Including your target keyword in your page’s body text, especially in the beginning of the copy and in the heading tags, is a strong relevance signal to Google. Remember that your H1 tag holds the most SEO weight out of all heading tags.

If your page does not have an H1 tag, or if you can’t tell where it is, click Edit source. Locate your H1 (to do it quickly, hit Ctrl + F and run a search for “<h1”) and edit it right in the page’s source code, like you would in an HTML editor. If the search returns no results, you can create an H1 tag in this view. It’s generally recommended to put your header tag right above the page’s main content, preferably at the top of the <body> tag. To create your H1, simply type <h1>Any text you want to put in your header</h1> at the beginning of the page’s body.
If you’re looking to optimize the page even further, and if your content is long enough to be using multiple headings, repeat the process above for your H2-H6 tags. However, make sure you don’t overuse the same keywords to avoid keyword stuffing; instead, think of related topics with the same user intent behind them.
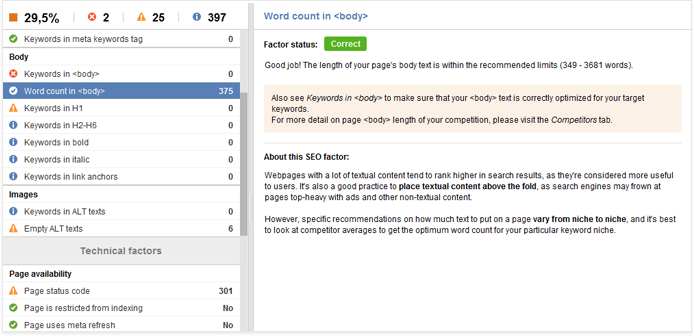
7. Content length
In its search quality guidelines, Google mentions the length of content as an important criterion for the page’s quality — and therefore its rankings. Clearly, there’s no ideal content length you should aim for; still, the SEO world is full of misconceptions like “longer content ranks better” and “your copy should be over 2,000 characters long to rank in top 10”. These assumptions do have their ground, but it’s important to understand that the elusive “ideal content length” may vary a lot from niche to niche. For a realistic reference on the right size for your content, it’s best to look at pages that already rank well for the keywords you’re targeting.
8. Unique content
Not surprisingly, your content has to be original to rank well in Google. It doesn’t even matter much what your site is about — starting from blog posts and on to e-commerce product pages, you need to bring unqiue value to the table if you are aiming for top rankings. In fact, plagiarized copy and duplicate product descriptions can well get you penalized by Google’s Panda update.
But are you totally safe if you haven’t been stealing anyone’s writing and put up all the content on your site yourself? Not necessarily. The trick is, Google may not always be able to identify the original if it’s given two instances of very similar content. And yes, that means being stolen from can sometimes get you in trouble, too.
Technical site factors (0.5 oz)
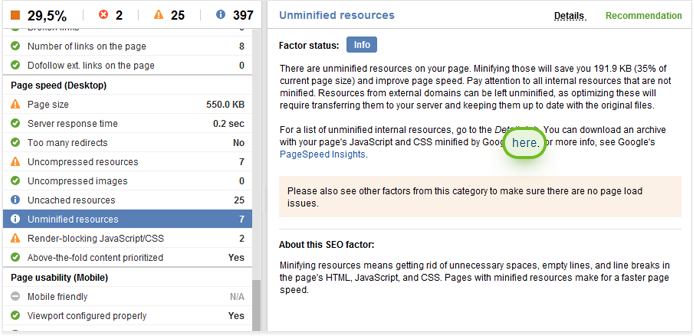
9. Page speed
Google has officially confirmed that it uses page speed in its ranking algorithm. Page speed can also influence your SEO indirectly, as search engines will likely crawl fewer pages if your site is slow due to the allocated crawl budget. This, in turn, could negatively affect your site’s indexation.
Load time can have a massive impact on user experience, too. Slower pages tend to have higher bounce rates and lower average time on page. Research shows a 1-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% reduction in conversions.
So what’s the page speed you should aim for? Google’s mentioned they expect pages to load in 2 seconds or less.
If there’re any Uncompressed images or Unminified resources found on your page, jump to the Recommendation tab for a ready-made compressed version of your images and JS/CSS. Follow the link to download the lighter version of those, and feel free to upload them to your site right away.
10. Mobile friendliness
With over half of Google searches coming from mobile devices, Google’s increasing focus on improving mobile search results is only fair. From a nice-to-have, mobile friendliness has turned into a must — if your page isn’t optimized for mobile devices, it’s likely to be discarded from mobile search results completely.
The factors in the Page usability (Mobile) section are the exact features Google believes mobile-friendly pages should have, according to Google Developers’ PageSpeed Insights, so you’ll want all of them to be marked with a green Correct sign.
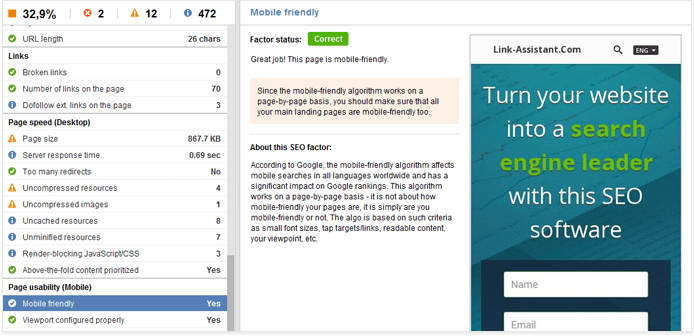
If your page isn’t mobile friendly altogether, there isn’t a better time to optimize for mobile than now. While there’s a bunch of options available, responsive design is perhaps the simplest and most widely used solution — and it’s the one Google recommends, too. If you use WordPress (or any CMS, really), choosing a responsive template for your site is about all it takes.
You’re in for more work if your site is HTML-coded with no CMS in place. However, there’s a bunch of documentation available on adapting responsive design for web developers. It might take a bit of work to get every aspect right, but it’s an investment that’ll definitely keep paying off increasingly.
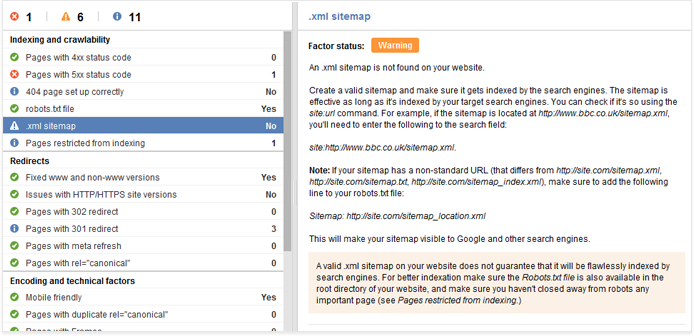
11. Sitemap
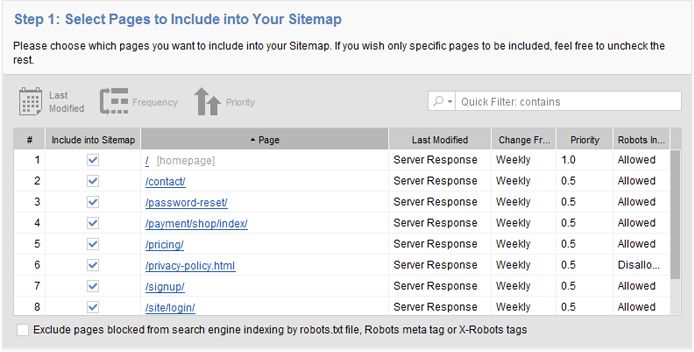
Okay, strictly speaking, having a sitemap is not a ranking factor — as in, it won’t actually help your site rank higher. But an XML sitemap will help Google spider your site, and make sure it can index your pages quickly and easily. It is the simplest and most effective way to tell Google what pages your site includes.
User Experience & Trust (1.5 oz)
12. Click-through rate
Numerous patents filed by Google along with real-life experements show that SERP click-through rates can have a massive impact on rankings. A click-through rate, or CTR, is a ratio of the number of times a given search listing was clicked on to the number of times it was displayed to searchers.
For every query, Google expects a CTR in a certain range for each of the listings (e.g. for branded keywords, the CTR of No.1 result is around 50%; for non-branded queries, the top result gets around 33% of clicks). If a given listing gets a CTR that is seriously above (or below) that range, Google can re-rank the result accordingly.
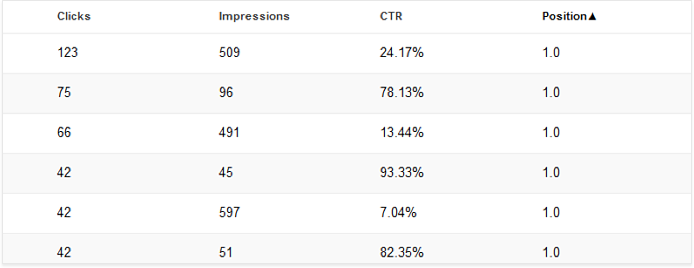
While CTR values for different positions in Google SERPs can vary depending on the type of the query, on average, you can expect at least 30% of clicks for a No.1 result, 15% for a No.2 result, and 10% for a No.3 result.
If the CTR for some of your listings is seriously below these averages, these could be the problem listings you’d want to focus on in the first place.
So the only way to make your listing earn actual clicks from real users is to make it appealing and click-worthy. As you remember, you can edit and preview your Google snippet in Content Analysis -> Content Editor in WebSite Auditor, under the Title & Meta tags tab.
As you compose your title and description, make sure they clearly communicate the value of clicking through to your page to searchers. If appropriate, use a call to action and instead of simply describing what your page is about, address the searcher directly, and inform them about the benefits of navigating to your page, choosing your product, and so on.
Once you’re happy with your snippet, hit Save page to save the upload-ready HTML file to your hard drive.
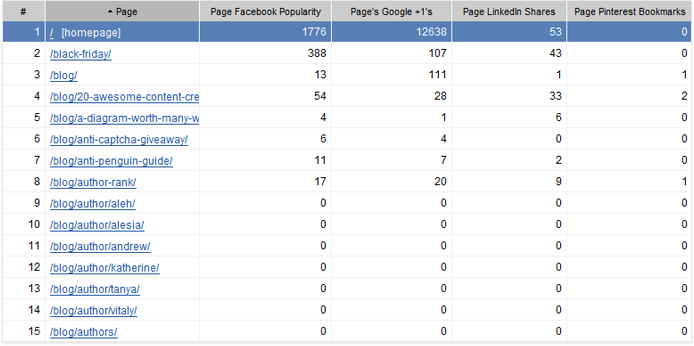
13. Social signals
The discussion on whether or not social signals affect rankings directly is ongoing, and some real-life experiments seem to prove it’s causation, not correlation. Or is it? Google’s never confirmed it, but one thing we do know for sure is that pages with more social shares rank better. Period.
Now that you’ve got the necessary prerequisites in place, you’ve got to think about distributing your content for maximum exposure. Whatever your promotion strategy is (email marketing, social media marketing, or influencer outreach), remember that you need content that is truly unique and useful to be successful. If you’re only starting out at social media, here’s a great guide on social content promotion that can also help SEO and brand awareness.
One last thing…
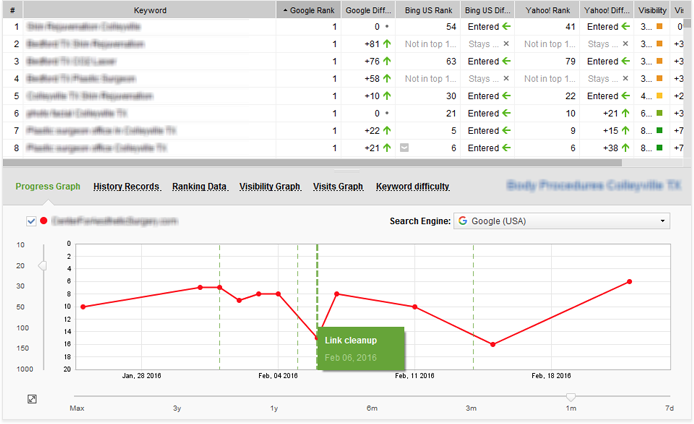
Apparently, the best way to understand which of the signals above are making the biggest impact in your niche is to try them yourself and track progress. One great way of doing that is using SEO PowerSuite’s Rank Tracker to monitor your Google rankings, and document the SEO changes you make with Rank Tracker’s Events. To do that, open your Rank Tracker project. Go to Preferences -> Events and click Add. Briefly describe the event and set a date for it. On the progress graph in Rank Tracker, you will now easily see how your SEO changes are affecting your rankings, and which ones have bigger impact than others.